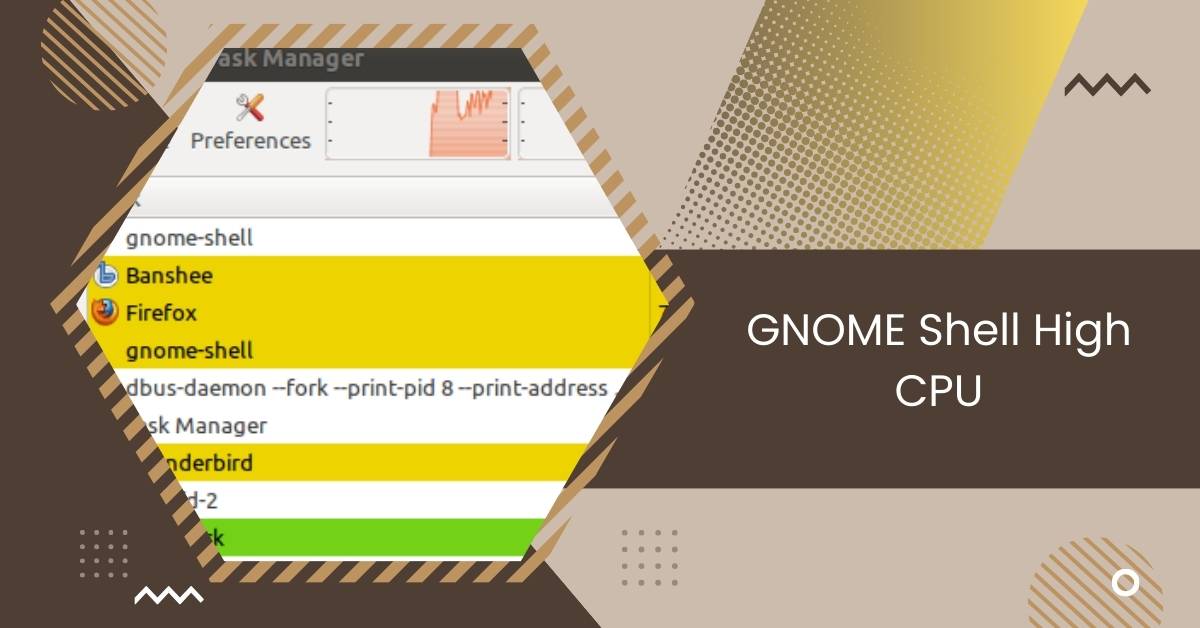
Experiencing high CPU usage with Gnome Shell could indicate software bugs or resource-heavy tasks. Consider updating Gnome Shell and monitoring system resources for improvement.
This article will look into why GNOME Shell might use a lot of your computer’s CPU and offer ways to fix these problems.
Understanding High CPU Usage
1. What Causes High CPU Usage?
High CPU usage occurs when the processor works harder than usual to execute tasks. In the context of GNOME Shell, this can happen due to various factors such as resource-intensive applications, malfunctioning extensions, or system misconfigurations.
2. Impact of High CPU on System Performance
High CPU usage can significantly impact system performance, leading to sluggishness, unresponsiveness, and decreased overall productivity. It can also increase power consumption, affecting battery life on laptops and mobile devices.
Why Does GNOME Shell High CPU?
1. Extensions
Including extensions in GNOME Shell can enhance your computer’s functionality, yet poorly coded or outdated ones may strain the CPU unnecessarily. To resolve this problem, simply disable or uninstall the troublesome extensions.
2. Resource-Intensive Activities
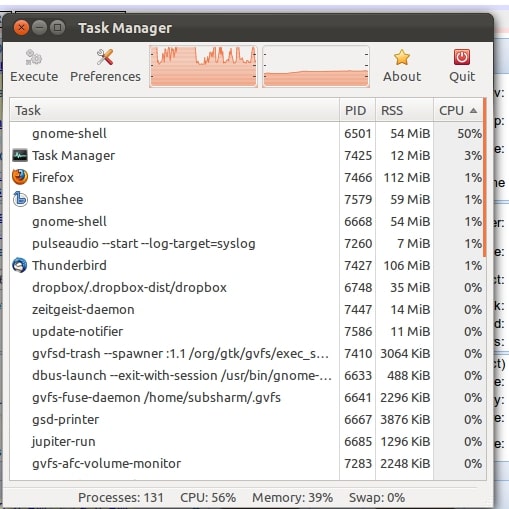
If you use resource-intensive applications like video editors or virtual machines, GNOME Shell may experience higher CPU usage.
In such cases, the responsibility for the increased CPU usage lies with the applications running on GNOME Shell.
See Also: Why Does My CPU Fan Start And Stop – The Ultimate Overview
3. Background Processes
Background tasks such as indexing and thumbnail creation can consume significant CPU resources on your computer.
When you add or modify files, the system may automatically organize them to facilitate easier searching. You can adjust these settings to optimize system performance.
4. Driver Issues
Problems with graphics drivers, particularly those provided by GPU manufacturers like NVIDIA, can impact CPU power consumption.
It’s essential to ensure your computer has the latest and correct hardware drivers installed.
5. Outdated Software
Using an outdated version of GNOME Shell can result in sluggish performance and excessive CPU usage on your computer.
To address this issue, update to the latest version, which can resolve known issues and improve overall speed.
6. Extensions Conflicts
Issues may arise when various GNOME Shell plugins need to collaborate effectively, causing excessive CPU usage.
To identify the culprit, try enabling or disabling each plugin individually to pinpoint the one causing the problem.
See Also: High CPU Temp On Startup – Fix Startup CPU Overheating Now!
How To Fix GNOME Shell CPU High?
1. Check For Gnome Shell Extensions
- Open your web browser and go to the GNOME Extensions website.
- Install the GNOME Shell Integration extension for your browser. This helps you control extensions right from your browser.
- Click on the Integration extension icon in your browser.
- Check the extensions you’ve installed and see which ones are turned on.
- Make sure your extensions work well with your GNOME Shell version.
- Sometimes, extensions might not work correctly with newer GNOME Shell versions, causing performance problems.
- Keep an eye out for updates to your extensions.
- Developers often release updates to fix issues and make extensions work better with the latest software, improving performance.
2. Reduce Gnome Shell Animations
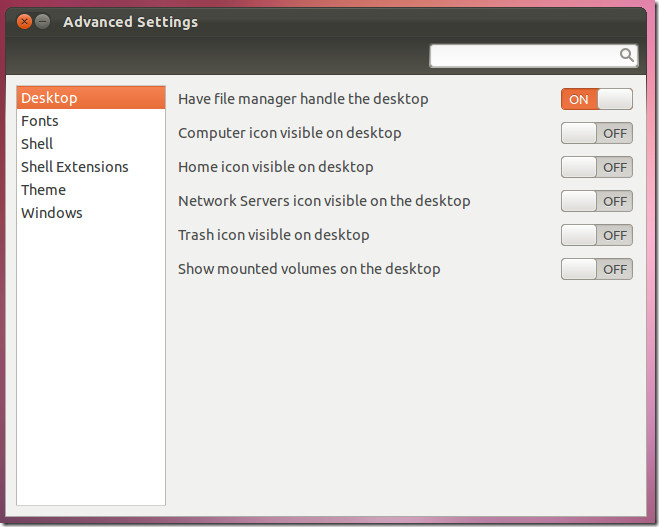
Even though the animations in GNOME Shell look nice, they can use much of your computer’s power. You can use GNOME Tweaks to control them:
- If you still need to add GNOME Tweaks, use your package manager.
- Open GNOME Tweaks and go to the “Appearance” section.
- Adjust or turn off the effects according to your preference.
3. Check For Graphics Driver Updates
Ensure your computer has the most up-to-date graphics drivers. Outdated or incorrect drivers often lead to high CPU usage.
To check and install drivers from a specific company, like NVIDIA:
Use the command: sudo pacman -S Nvidia.
4. Evaluate Desktop Background
A complex or high-resolution desktop background can sometimes make your CPU work harder. Consider changing the background to something more straightforward to reduce the strain on your CPU.
See Also: Swapped CPU Now No Display – Resolve All Issues – 2024!
5. Check Resource-Hungry Applications
Background applications using lots of CPU can make GNOME Shell slow. Use system tracking tools like “htop” or the system monitor to find processes using too many resources. If you have extra programs running, consider closing or removing them from your computer.
To add “htop”
Use the command: sudo pacman -S htop
6. Review Gnome Shell Settings
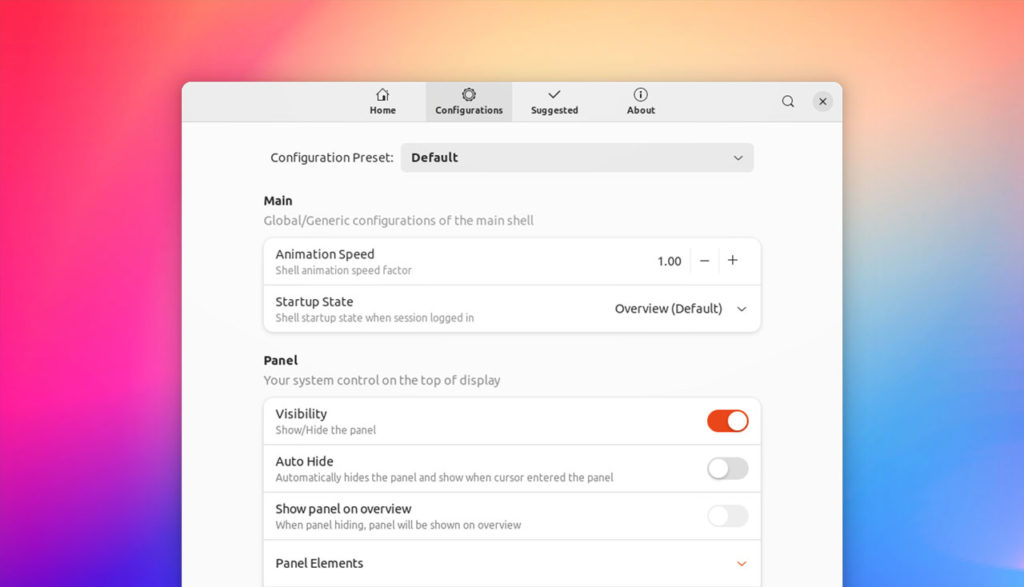
To decrease CPU usage, you can adjust GNOME Shell settings. Open the GNOME Tweaks tool and navigate to the “Appearance” tab. Lower the settings for animations and effects, or disable them altogether.
7. Switch From Wayland To Xorg
Sometimes, if you use GNOME on Wayland, it can make your CPU work harder. To switch to Xorg, you can change your display manager configuration. Usually, you’d edit the /etc/gdm/custom.conf file and set WaylandEnable=false.
Use this command: sudo nano /etc/gdm/custom.conf
Make sure Wayland is disabled and the GNOME session is running on Xorg.
8. Evaluate Third-Party Tools
Additional tools can offer assistance but may also strain your CPU. Assess their impact on your system and contemplate using alternatives that are better suited to your computer’s capabilities.
9. Kernel Rollback
If you suspect that a kernel change is causing issues, you can revert to the previous version (5.19.0-45) and verify if the problem persists.
You can select the older kernel version from the GRUB menu during the boot process to perform this action. If the issue disappears with the old kernel, it’s likely caused by the new kernel.
10. Review Unattended Upgrades
As the issue coincided with an automatic kernel update, examine the logs for any changes that occurred without your intervention.
Investigate whether there are any known issues associated with your current kernel version. Updates to the kernel can occasionally introduce problems that lead to increased CPU usage.
See Also: CPU Vdd Soc Current Optimization – Optimize CPU Power!
How To find the cause for high CPU usage of gnome-shell?
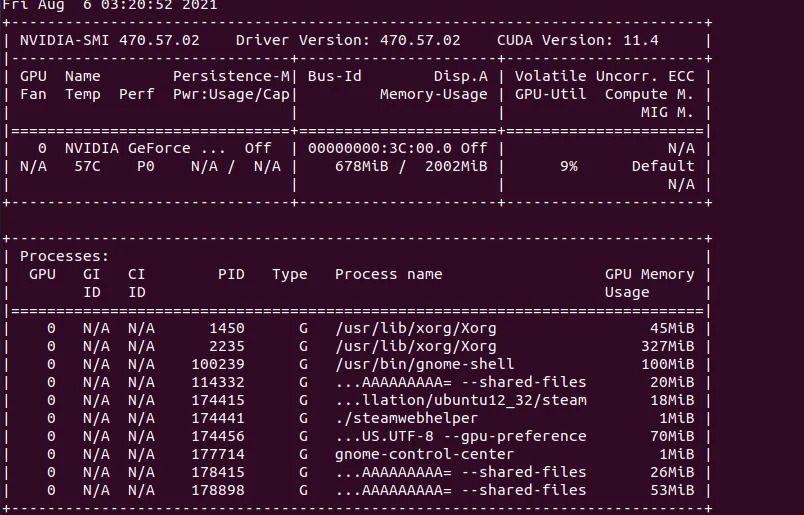
Here are a couple of potential reasons:
- To eliminate the seconds from the clock, execute the command: `gsettings set org.gnome.desktop.interface clock-show-seconds false`
- Look for ‘System Load Indicator’ in the menu for a CPU usage monitor. Stop the process and turn off autostart, or set a longer probing time, like 10 seconds, to make it less resource-intensive.
- Be cautious of any applications with real-time monitoring for disk, CPU, or network activities.
Fedora Gnome-Shell High CPU
Fedora’s GNOME Shell can sometimes use too much CPU due to software bugs, heavy extensions, or system settings. Updating GNOME, managing extensions, and optimizing settings can help reduce CPU usage.
See Also: How To Reset Overclock CPU – Improve CPU Speed In 2024!
Ubuntu 22.04 Gnome-Shell High CPU
Ubuntu 22.04’s GNOME Shell might use too much CPU due to bugs, resource-heavy extensions, or certain settings. Updating GNOME, managing extensions, and tweaking settings can help lower the CPU usage.
Ubuntu 22.04 gnome-shell has a high CPU usage of up to 1600%
Ubuntu 22.04’s GNOME Shell can use up to 1600% CPU due to bugs, heavy extensions, or system settings. Updating GNOME, managing extensions, and adjusting settings can help reduce this high CPU usage.
Ubuntu 18.04 gnome-shell high CPU usage
Ubuntu 18.04’s GNOME Shell may use too much CPU due to bugs, heavy extensions, or settings. Updating GNOME, managing extensions, and adjusting settings can lower CPU usage.
Ubuntu 20.04 gnome-shell continual 20% CPU usage
Ubuntu 20.04’s GNOME Shell might constantly use 20% CPU due to extensions, bugs, or settings. Updating GNOME, disabling extensions, and optimizing system settings can help reduce this CPU usage.
Ubuntu 20.04 Gnome-Shell Extension CPU Usage
In Ubuntu 20.04, GNOME Shell extensions can increase CPU usage. Disable unnecessary extensions, update GNOME Shell and manage settings to reduce CPU load and improve system performance.
Gnome shell increasing cpu usage over time, why does it and how can I fix it?
GNOME Shell’s CPU usage may increase over time due to memory leaks, software bugs, or resource-intensive processes. To fix it, try updating GNOME Shell, managing extensions, and monitoring system resources regularly.
High CPU usage (gnome shell, firefox)
High CPU usage, especially with GNOME Shell and Firefox, can occur due to resource-intensive tasks, software bugs, or excessive background processes. Solutions include updating software, managing extensions, and optimizing system settings.
Gnome-shell high CPU usage when mouse moves
High CPU usage by GNOME Shell when moving the mouse could indicate a graphics driver issue or a bug in the desktop environment. Try updating drivers and GNOME Shell, turning off unnecessary extensions, and monitoring system resources for improvements.
See Also: CPU Userbenchmark Bias – Investigate CPU Test Equality!
Rising CPU usage of gnome-shell after a while, when moving mouse in Pop!_OS 21.04
The increasing CPU usage of GNOME Shell in Pop!_OS 21.04 when moving the mouse might be due to software bugs or system resource issues. Consider updating GNOME Shell, managing extensions, and monitoring system resources for improvement.
Gnome-shell going to 100% CPU after clicking Ubuntu Software
If GNOME Shell spikes to 100% CPU usage after clicking Ubuntu Software, it could be due to a bug or a resource-intensive process. Try updating GNOME Shell, checking for software updates, and monitoring system resources for improvement.
Does anyone else have seriously high CPU usage with Gnome?
Yes, many users report experiencing high CPU usage with GNOME Shell. This can occur for various reasons, such as software bugs, resource-intensive processes, or incompatible extensions.
Gnome-shell occasionally eating CPU in Ubuntu 22.04.1
GNOME Shell’s occasional high CPU usage in Ubuntu 22.04.1 might stem from software glitches or resource-heavy tasks. Consider updating GNOME Shell, managing extensions, and monitoring system performance for improvements.
Gnome-shell uses up to 40% CPU by just gently moving mouse
Gnome-shell consuming up to 40% CPU while gently moving the mouse could indicate a performance issue. Try updating GNOME Shell, checking for system updates, and monitoring resource usage to identify and resolve the problem.
GNOME Shell: Abnormal CPU usage on mouse input.
Experiencing abnormal CPU usage in GNOME Shell when using the mouse input might indicate a software issue. Consider updating GNOME Shell, checking for system updates, and monitoring CPU usage to address the problem.
See Also: CPU Core Ratio Sync All Cores Or Auto – System Optimization!
Laggy Gnome 3.28.2 and gnome-shell high CPU usage
Experiencing lag and high CPU usage with Gnome 3.28.2 and Gnome-shell could result from software bugs or system resource limitations. To improve performance, consider updating Gnome, checking for system updates, and optimizing system settings.
Gnome-shell (gnome 3 ) uses large amount of CPU
In a Gnome shell, particularly in Gnome 3, consuming a significant amount of CPU might be due to software bugs or resource-intensive processes. Consider updating Gnome Shell, managing extensions, and monitoring system resources for improvement.
Getting really high CPU usage by gnome-shell after 3.24 upgrade
Gnome-shell’s significantly high CPU usage after upgrading to version 3.24 could be due to compatibility issues or software bugs. To address the problem, consider updating the gnome shell, checking for system updates, and monitoring CPU usage.
Gnome Shell high CPU usage after upgrade
Experiencing high CPU usage by Gnome Shell after an upgrade could be due to software bugs or compatibility issues. Try updating Gnome Shell, checking for system updates, and monitoring CPU usage for improvements.
Without a reason gnome-shell CPU usage gets high
Gnome-shell CPU usage inexplicably rises without a clear reason. This could indicate software bugs or resource-intensive processes. Consider updating Gnome-shell, checking for system updates, and monitoring CPU usage for improvements.
Ubuntu 20.04 gnome-shell high CPU usage
Experiencing high CPU usage with gnome-shell in Ubuntu 20.04 could be due to software bugs, resource-intensive processes, or incompatible extensions. Consider updating gnome-shell, managing extensions, and monitoring system resources for improvement.
See Also: Windows XP CPU Support List – Click For The Shocking Guide!
Gnome-shell CPU usage high
Experiencing high CPU usage with gnome-shell could indicate software bugs, resource-heavy tasks, or incompatible extensions. Consider updating gnome-shell, managing extensions, and monitoring system resources for improvement.
Gnome-shell 99% CPU usage and desktop unresponsive
Experiencing 99% CPU usage by gnome-shell, causing desktop unresponsiveness, could be due to software bugs or resource-intensive processes. Try updating gnome-shell, checking for system updates, and monitoring CPU usage for improvement.
Gnome-shell high CPU RHEL 8
Experiencing high CPU usage with gnome-shell on RHEL 8 might be due to software bugs or resource-heavy tasks. Try updating gnome-shell, managing extensions, and monitoring system resources for improvement.
Gnome-shell high memory
Experiencing high memory usage with gnome-shell could indicate software bugs or resource-intensive processes. Try updating gnome-shell, managing extensions, and monitoring system resources for improvement.
Gnome-shell high CPU moving mouse
Experiencing high CPU usage in Gnome Shell when moving the mouse could be due to software bugs or inefficient resource management. Try updating Gnome Shell, checking for system updates, and monitoring CPU usage for improvement.
Gnome shell high CPU centos 7
Experiencing high CPU usage with gnome-shell on CentOS 7 might be due to software bugs or resource-heavy processes. Consider updating gnome-shell, managing extensions, and monitoring system resources for improvement.
Gnome shell high CPU Fix
To fix high CPU usage with Gnome Shell, try updating Gnome Shell, managing extensions, and monitoring system resources for improvements. Additionally, check for software updates and optimize system settings for better performance.
See Also: Why Is My CPU Usage So Low While Gaming: Fix Issues – 2024
Common Reasons for High CPU Usage in GNOME Shell
- Extensions: Resource-heavy or poorly optimized extensions can cause GNOME Shell to consume excessive CPU.
- Bugs: Software bugs or glitches in GNOME Shell or related components can lead to high CPU usage.
- System Settings: Inefficient system configurations, such as high-resolution displays or multiple monitors, can increase CPU load.
Troubleshooting High CPU Usage in GNOME Shell
- Update GNOME Shell: Ensure you’re using the latest version to benefit from bug fixes and performance improvements.
- Disable Extensions: Turn off all extensions and re-enable them one by one to find any causing high CPU usage.
- Adjust Settings: Lower display resolution and tweak system performance settings to reduce CPU load.
- Check System Logs: Use tools like journalctl to identify errors or conflicts that might be causing high CPU usage.
See Also: CPU Usage Drops When I Open Task Manager – Ultimate Guide!
Frequently Ask Questions
1. Is It Safe To Remove Gnome Shell?
It’s not safe to remove GNOME Shell because it’s a crucial part of the GNOME desktop experience. Removing it could make the system less stable. Instead, focus on fixing any issues you encounter.
2. What Should I Do If Gnome Shell Remains Unresponsive?
You can restart if GNOME Shell isn’t working or uses too much CPU. Press Alt + F2, type ‘r,’ and press Enter. This often solves Small issues.
3. Is Gnome Shell Available On Other Linux Distributions Besides Ubuntu?
GNOME Shell is found on many Linux systems, like CentOS 7. It gives you a friendly desktop and is commonly used on various Linux systems.
4. Does Gnome Use A Lot Of Memory?
Yes, GNOME can use a large amount of memory. If it’s using 12GB or more, that’s usually a sign of a problem that needs fixing. Regularly maintaining and monitoring your system can help keep memory usage reasonable.
5. How do I check CPU usage in GNOME Shell?
You can use system monitoring tools like GNOME System Monitor or the top command in the terminal to check CPU usage.
6. Why is my GNOME Shell consuming high CPU resources?
High CPU usage in GNOME Shell can occur due to various factors such as incompatible extensions, resource-intensive applications, or system misconfigurations.
7. Can I optimize GNOME Shell for better performance?
Yes, you can optimize GNOME Shell by managing extensions, adjusting system settings, and keeping your software up to date.
8. Will restarting GNOME Shell fix high CPU usage issues?
Restarting GNOME Shell can sometimes resolve temporary issues caused by misbehaving processes or memory leaks, but it may not always fix underlying problems.
Conclusion
To resolve high CPU usage in GNOME Shell, address common causes such as problematic extensions, resource-intensive apps, and outdated graphics drivers.
Optimize system settings, reduce animations, and switch to Xorg if necessary. Regular maintenance, monitoring, and staying updated can enhance overall performance.
Read More
- Pfsense CPU Doesn’t Support Long Mode – Solutions In 2024!
- Cannot Pin ‘Torch.Cuda.Longtensor’ Only Dense CPU Tensors Can Be Pinned
- Is Execution Time The Same As CPU Time – Ultimate Guideline!

Hi everyone, Johns Jack here, your approachable tech aficionado! I’m passionate about CPUs and thrive on keeping up with the newest tech developments. Join me as we delve into the dynamic realm of technology! Visit: Techy Impacts