If you have a passion for gaming or engage in resource-intensive tasks like video editing or 3D rendering, you’ve likely encountered the terms “GPU bottleneck” and “CPU bottleneck.”
Yes, your GPU can bottleneck your CPU if it’s unable to keep up with the processing demands, leading to performance issues like low frame rates and stuttering during tasks like gaming or rendering.
Let’s delve into the world of hardware bottlenecks and find out how they affect your computing experience.
Introduction
In the world of technology, two essential components play a crucial role in determining the performance of your system: the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) and the Central Processing Unit (CPU).
Understanding how these components interact and whether your GPU could bottleneck your CPU is vital for optimizing your system’s efficiency.
Definition of GPU and CPU

The GPU is responsible for handling graphics-intensive tasks, such as rendering images and videos, while the CPU manages general computing tasks and processes.
Both work together to ensure smooth operation and performance of your computer.
Importance of balanced performance between GPU and CPU
A well-balanced GPU-CPU performance is key to achieving optimal performance in gaming, video editing, 3D modeling, and other demanding tasks.
A bottleneck, where one component restricts the performance of the other, can hinder your system’s capabilities.
Read: CPU Usage Drops When I Open Task Manager – Ultimate Guide!
Overview of how a bottleneck occurs in a system
A bottleneck can occur when one component, typically the GPU or CPU, is significantly faster or slower than the other, leading to a performance mismatch.
This can result in reduced frame rates, slower rendering times, and overall sluggish system performance.
Factors Influencing GPU-CPU Interaction
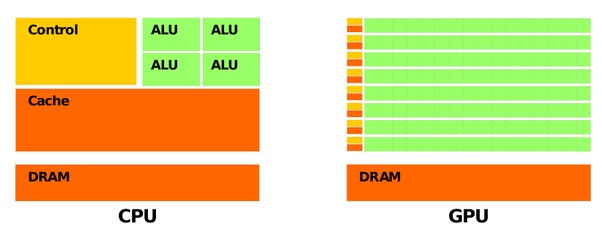
To determine whether your GPU might bottleneck your CPU, consider the following factors:
1. GPU and CPU specifications
The specifications of your GPU and CPU, such as clock speed, core count, and architecture, determine their processing capabilities. Mismatched specifications can lead to a bottleneck.
2. Workload distribution between GPU and CPU
Certain tasks rely more heavily on either the GPU or CPU. Ensuring that the workload is distributed effectively between the two components can prevent bottlenecks.
3. Compatibility between GPU and CPU
Compatibility issues between your GPU and CPU, such as driver conflicts or system requirements, can also contribute to bottlenecking issues.
4. Identifying a Bottleneck
To identify whether your GPU is bottlenecking your CPU, follow these steps:
5. Monitoring GPU and CPU performance
Use monitoring software to track the performance of your GPU and CPU during various tasks. Look for instances where one component maxes out while the other remains underutilized.
6. Analyzing system benchmarks
Run benchmarks to assess the overall performance of your system. Look for disparities in performance between the GPU and CPU, which may indicate a bottleneck.
7. Understanding the impact of a bottleneck on overall performance
A bottleneck can result in reduced frame rates, stuttering, and slower load times in games and applications. Identifying and addressing bottlenecks is crucial for optimizing system performance.
Read: Process Lasso Error Setting Process CPU Affinity – Resolve!
Resolving GPU-CPU Bottleneck
If you suspect a bottleneck in your system, consider the following solutions:
1. Upgrading GPU or CPU
Upgrading either the GPU or CPU to better match the processing capabilities of the other component can alleviate bottlenecks and improve overall performance.
2. Optimizing software and drivers
Updating drivers, optimizing software settings, and ensuring compatibility between components can help resolve bottlenecking issues. Adjusting system settings for better resource allocation
Adjusting settings in games and applications to distribute the workload more evenly between the GPU and CPU can help prevent bottlenecks.
How to balance GPU and CPU performance
1. Choosing compatible hardware
Selecting hardware components that are well-matched in terms of performance capabilities can help ensure balanced GPU and CPU performance and minimize the risk of bottlenecks.
2. Tweaking settings
Experimenting with graphics settings, adjusting overclocking parameters, and optimizing software configurations can help achieve a balance between GPU and CPU performance for optimal system operation.
Future-proofing your System
To ensure optimal performance in the long run, consider the following strategies:
1. Keeping up with technological advancements
Stay informed about the latest GPU and CPU technologies to make informed upgrade decisions and prevent potential bottlenecks.
2. Planning for potential upgrades
Anticipate future upgrades to your system, considering the compatibility and balance between your GPU and CPU to prevent bottlenecking issues.
3. Maintaining a balanced GPU-CPU performance for optimal system efficiency
Regularly monitor your system performance and take proactive steps to maintain a balanced GPU-CPU performance for optimal efficiency.
Read: CPU Maximum Frequency Always 100 – Ultimate Guide – 2024!
FAQs
1. How can I determine if my GPU is bottlenecking my CPU?
To determine if your GPU is bottlenecking your CPU, monitor their usage during tasks. If the CPU is consistently at maximum capacity while the GPU is underutilized, it indicates a potential bottleneck.
2. What are some common signs of a GPU-CPU bottleneck?
Common signs of a GPU-CPU bottleneck include reduced frame rates, stuttering, and longer rendering times in games or applications.
3. Is it better to upgrade the GPU or CPU to resolve a bottleneck?
Whether to upgrade the GPU or CPU depends on the specific bottleneck scenario. If the GPU is the bottleneck, upgrading it will likely yield more significant performance improvements.
4. Can software optimization help alleviate a GPU-CPU bottleneck?
Yes, software optimization can help alleviate a GPU-CPU bottleneck by optimizing workload distribution, updating drivers, and adjusting system settings for better resource allocation.
5. How frequently should I check for a GPU-CPU bottleneck in my system?
It’s advisable to check for a GPU-CPU bottleneck periodically, especially after system updates or when encountering performance issues. Checking every few months or when upgrading hardware is a good practice.
6. How can I tell if my system is experiencing GPU bottlenecking?
Look for indicators such as high GPU utilization and low CPU utilization, inconsistent frame rates, and visual artifacts during gameplay.
7. What are some signs of CPU bottlenecking?
Signs of CPU bottlenecking include high CPU utilization, slow processing times, and system slowdowns during multitasking.
8. Can bottlenecking be completely eliminated?
While bottlenecking can be minimized through hardware upgrades and software optimization, completely eliminating it may not always be possible, especially in demanding applications.
9. Is overclocking a viable solution for addressing bottlenecking?
Overclocking can potentially improve performance but may also increase the risk of hardware damage and instability if not done properly.
10. Are there any software tools available for diagnosing bottleneck issues?
Yes, various software utilities provide real-time monitoring and diagnostics for identifying bottleneck issues, such as MSI Afterburner and CPU-Z.
Conclusion
Final Words,
Understanding the interaction between your GPU and CPU is crucial for optimizing system performance.
By identifying and addressing potential bottlenecks through hardware upgrades and software optimization, you can ensure smoother operation and enhanced computing experiences.
Also Read
- AVConferenced CPU – Boost Your Conference Experience – 2024
- What CPU Will Bottleneck A Rtx 3060 – Check Bottleneck Risk!
- Is 40c Good For CPU – Find Out If 40°C Perfect Temperature!

Hi everyone, Johns Jack here, your approachable tech aficionado! I’m passionate about CPUs and thrive on keeping up with the newest tech developments. Join me as we delve into the dynamic realm of technology! Visit: Techy Impacts

