When diving into gaming, understanding the intricacies of your computer’s hardware performance becomes crucial.
Low CPU usage while gaming may suggest ineffective GPU utilization, potentially causing performance bottlenecks. To optimize performance, ensure CPU and GPU are adequately utilized, considering factors like game optimization and hardware limitations.
In this article, we’ll unravel the mysteries behind this phenomenon and explain why your CPU usage might be low while gaming.
What is CPU usage?
CPU usage refers to the percentage of a CPU’s processing capacity actively utilized at any given time. It reflects the amount of computational work the CPU performs, including executing instructions, processing data, and managing system tasks.
Monitoring CPU usage is essential for assessing system performance, diagnosing bottlenecks, and optimizing resource allocation.
Understanding CPU usage allows users to identify when the CPU is under stress or operating at its maximum capacity, which can affect overall system responsiveness and performance.
Factors Affecting CPU Usage During Gaming

- Graphics Settings: The resolution, texture quality, shadow details, and other graphical settings in a game can significantly impact CPU usage. Higher settings often require more processing power to render complex visuals.
- Game Optimization: Well-optimized games distribute computational tasks efficiently across CPU cores, leading to balanced CPU utilization. Poorly optimized games may strain the CPU, resulting in higher usage.
- Background Processes: Background applications running concurrently with the game can consume CPU resources, reducing the available processing power for gaming tasks. Closing unnecessary programs can alleviate this issue.
- Hardware Limitations: The specifications of the CPU itself, such as clock speed, core count, and architecture, play a crucial role in determining its performance during gaming. Older or lower-tier CPUs may need help to keep up with the demands of modern games.
- Multiplayer Networking: In multiplayer games, the CPU may need to handle additional networking-related tasks, such as player synchronization, latency compensation, and server communication. This can increase CPU usage compared to single-player games.
- Physics Calculations: Games with advanced physics engines require the CPU to perform real-time calculations for interactions between objects, characters, and environments. Complex physics simulations can result in higher CPU usage.
- AI Processing: Games featuring sophisticated artificial intelligence (AI) systems rely on the CPU to handle AI behaviours, decision-making, and pathfinding for non-player characters (NPCs). More intelligent and dynamic AI can lead to higher CPU usage.
- Scripting and Mods: User-generated content, scripting languages, and mods can introduce additional computational overhead, as the CPU needs to interpret and execute custom scripts or modifications. This can vary depending on the complexity and quantity of mods installed.
- Screen Resolution and Refresh Rate: Higher screen resolutions and refresh rates require more CPU resources to render frames and maintain smooth gameplay. Increasing resolution or refresh rate settings can lead to higher CPU usage.
- Operating System Overhead: The operating system running on the computer also imposes its overhead regarding system processes, background services, and resource management. Optimizing system settings and minimizing unnecessary services can reduce OS-related CPU usage during gaming.
Low CPU usage while gaming: Causes and implications
- Efficient Game Optimization: Well-optimized games may exhibit lower CPU usage while maintaining optimal performance, indicating effective resource allocation and task distribution across CPU cores.
- GPU Bottlenecking: In some cases, the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) may become the bottleneck in a gaming setup, reaching its maximum capacity before the CPU. This can lead to lower CPU usage as the CPU waits for the GPU to process graphical tasks, potentially affecting overall gaming performance.
- Misinterpretation of CPU Usage: Low CPU usage during gaming doesn’t necessarily indicate inefficiency or underperformance. Specific game sequences or scenarios may not heavily tax the CPU, resulting in lower utilization without compromising gameplay quality.
- Optimized Background Processes: Efficient management of background processes and system tasks can lead to lower CPU usage during gaming. Background applications consuming fewer CPU resources leave more processing power available for gaming tasks, contributing to smoother gameplay experiences.
- Hardware Limitations: The specifications of the CPU, such as clock speed, core count, and architecture, can influence its performance during gaming. Older or lower-tier CPUs may exhibit lower usage due to hardware limitations, impacting overall gaming performance.
- Balanced Workload Distribution: Games that distribute computational tasks evenly across CPU cores can lower overall CPU usage while maintaining optimal performance. This balanced workload distribution ensures efficient utilization of available processing power.
- Reduced System Overhead: Minimizing system overhead, including unnecessary background processes, services, and applications, can lead to lower CPU usage during gaming. Optimizing system settings and configurations helps free up CPU resources for gaming tasks, improving overall performance.
- GPU Acceleration: Certain games leverage GPU acceleration for specific tasks, reducing the CPU’s workload and reducing CPU usage. GPU-accelerated features, such as physics simulations or post-processing effects, offload computational tasks from the CPU, improving overall efficiency.
- Limited Multithreading Support: Games that lack robust multithreading support may only partially utilize available CPU cores, leading to lower overall CPU usage. This limitation can affect performance in CPU-bound tasks and scenarios, potentially impacting gaming experiences.
- Real-Time Resource Allocation: Dynamic resource allocation mechanisms within games can adaptively adjust CPU usage based on current gameplay demands. Real-time optimization of CPU resources ensures efficient utilization and responsiveness, enhancing the gaming experience.
See Also: High CPU Temp On Startup – Fix Startup CPU Overheating Now!
Effects of low CPU usage on gaming performance
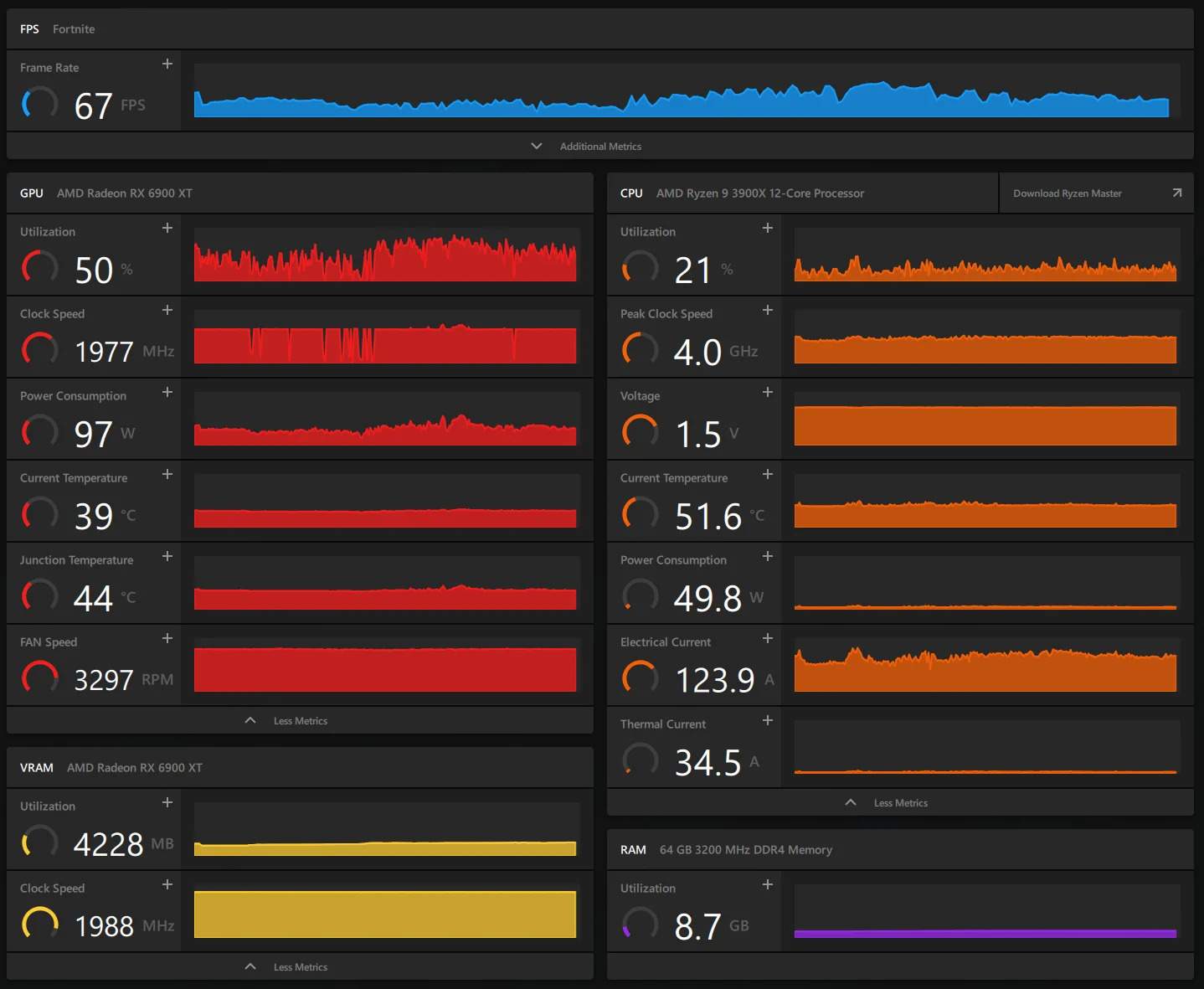
1. Smooth Gameplay Experience
A smooth gameplay experience is often achieved when optimized CPU usage, ensuring efficient resource allocation and responsiveness.
Lower CPU usage in well-optimized games can indicate the effective distribution of computational tasks, leading to fluid gameplay without frame drops or stuttering, enhancing the overall gaming experience.
2. Potential Bottleneck in CPU-Bound Tasks
A potential bottleneck in CPU-bound tasks arises when low CPU usage limits the performance of functions reliant on CPU processing power.
This can result in reduced frame rates, slower response times, and diminished overall gaming performance, primarily when the CPU is tasked with intensive computations or calculations.
3. Impact on Frame Rates and Responsiveness
The impact on frame rates and responsiveness is critical when assessing low CPU usage during gaming. Lower CPU usage can lead to decreased frame rates and slower responsiveness, particularly in CPU-bound scenarios where the CPU struggles to keep up with processing demands, resulting in less fluid gameplay and reduced user satisfaction.
How to interpret low CPU usage while gaming
Interpreting low CPU usage during gaming requires a comprehensive approach. Utilize monitoring tools to track CPU usage in real-time, comparing it with GPU usage and system performance indicators.
Benchmarking tests can provide insights into overall system performance, helping identify potential bottlenecks and optimize settings for an optimal gaming experience.
Troubleshooting Low CPU Usage Issues
1. Updating Drivers
Updating drivers is essential for optimal gaming performance. Outdated drivers can cause compatibility issues and performance bottlenecks.
Regular updates ensure efficient communication between hardware and software, maximizing stability and performance.
2. Adjusting In-Game Settings
Fine-tuning in-game settings is crucial for balancing performance and visual quality. Adjusting parameters like resolution and texture quality can optimize CPU and GPU workload, ensuring smooth gameplay without sacrificing graphics fidelity.
3. Overclocking
Overclocking involves boosting CPU performance beyond default settings. While it can enhance gaming performance, it requires caution.
Proper cooling and stability testing are vital to prevent overheating and ensure system reliability. Overclocking may void warranties and pose risks if done incorrectly.
See Also: Is 80c Safe For CPU – Check CPU Temperature For Safety!
Strategies to optimize CPU usage for gaming
1. Adjusting In-Game Settings
Adjusting in-game settings involves modifying graphical options, resolution, and other performance-related parameters to optimize CPU usage.
Lowering graphic settings can reduce the CPU workload, improving overall performance and enhancing the gaming experience on hardware-limited systems.
2. Updating Drivers and Software
Updating drivers and software is crucial for optimizing CPU performance during gaming. Ensuring that GPU drivers and game software are up to date can leverage optimizations and bug fixes, improving stability and enhancing overall system performance for a smoother gaming experience.
3. Closing Background Applications
Closing background applications is crucial to freeing CPU resources for gaming tasks. By minimizing unnecessary programs and services running in the background, users can reduce system overhead, improve CPU efficiency, and enhance overall gaming performance for a smoother experience.
4. Overclocking CPU for Enhanced Performance
Overclocking the CPU involves increasing its clock speed beyond the manufacturer’s specifications to achieve enhanced performance.
This can boost CPU performance during gaming by allowing it to process instructions faster, resulting in improved frame rates and overall responsiveness, albeit with potential risks such as increased heat generation and reduced stability.
Potential Issues with Low CPU Usage
- Bottlenecking: Low CPU usage may indicate that the CPU is not fully utilized, potentially causing bottlenecks in CPU-bound tasks and limiting overall system performance.
- Underutilization: Unused CPU capacity represents wasted resources, suggesting inefficiencies in task allocation or software optimization, which can hinder productivity and responsiveness.
- Inefficient Resource Allocation: Low CPU usage may result from poorly optimized software or inefficient resource allocation, leading to suboptimal performance and reduced productivity in multitasking environments.
- Performance Degradation: Persistently low CPU usage may indicate hardware or software issues, such as driver conflicts, malware infections, or hardware failures, which can degrade system performance over time.
- Compatibility Issues: Certain applications or games may not fully utilize the available CPU resources, leading to low CPU usage despite high demand, potentially causing compatibility issues and performance limitations.
- System Instability: In some cases, low CPU usage can be a symptom of underlying stability issues, such as overheating, voltage fluctuations, or insufficient power supply, resulting in system crashes or data loss if left unaddressed.
See Also: Is 70 Celsius Hot For CPU – Explore CPU Temperature Risks!
Related Questions
1. Why Is My CPU Usage So Low In-Game?
Low CPU usage in games can occur due to efficient game optimization, GPU bottlenecking, or misinterpretation of CPU usage. It’s not necessarily a problem if the game runs smoothly without performance issues.
2. How Can I Increase My CPU Usage For Games?
To increase game CPU usage, adjust in-game settings, update drivers, close background applications, and consider overclocking cautiously.
3. Why Is My CPU So Slow While Gaming?
Your CPU might need to be faster while gaming due to insufficient processing power, thermal throttling, outdated drivers, or background processes consuming resources. Consider upgrading hardware or optimizing settings for better performance.
4. What Is Normal CPU Usage When Gaming?
Normal CPU usage when gaming varies but typically ranges from 70% to 90%, depending on the game’s intensity, system specifications, and optimization.
5. CPU Usage 1 Percent While Gaming?
A CPU usage of 1% while gaming is shallow and may indicate an issue with monitoring software, misinterpretation of data, or a light gaming workload. It’s unusual and unlikely to reflect actual gaming performance.
6. How To Fix Low CPU Usage Windows 11?
To fix low CPU usage in Windows 11, update drivers, ensure power settings are optimized, scan for malware, turn off unnecessary startup programs and check for system updates. If issues persist, consider troubleshooting hardware or seeking professional assistance.
7. Why Is My CPU Usage So Low While Gaming Windows?
Low CPU usage while gaming on Windows may result from efficient game optimization, GPU bottlenecking, or misinterpretation of CPU usage. Ensure drivers are updated, background processes are minimized, and system resources are appropriately allocated for optimal performance.
Conclusion
In summary,
Monitoring and optimizing CPU usage during gaming is crucial for ensuring smooth performance and maximizing the gaming experience. Users can enhance system efficiency and enjoy a more enjoyable gaming experience by understanding the factors affecting CPU usage and addressing potential issues.
Read More
- What CPU Will Bottleneck A Rtx 3060 – Check Bottleneck Risk!
- Is Fortnite CPU or GPU Heavy – Find Best Setup For Fortnite!
- Does AMD GPU Work With Intel CPU – Explore Compatibility!

Hi everyone, Johns Jack here, your approachable tech aficionado! I’m passionate about CPUs and thrive on keeping up with the newest tech developments. Join me as we delve into the dynamic realm of technology! Visit: Techy Impacts

