In computer hardware, bottleneck discussions often center on the CPU or GPU.
Yes, a motherboard can bottleneck a CPU, mainly if it’s on a lower PCIe version. However, in most cases, motherboards don’t usually bottleneck CPUs unless there are compatibility or performance issues.
This article delves into the question: Can a motherboard bottleneck a CPU?
Understanding Bottlenecking
Bottlenecking happens when one part of a computer slows down another part. Imagine a road where cars move at different speeds.
If one section gets crowded, it slows down all the cars. In computers, parts like the CPU, GPU, RAM, and storage work together.
If one part is slow, it slows down everything. Even the motherboard, which connects all parts, can be a bottleneck.
If it’s not good enough, it can slow down the CPU. So, when building a computer, it’s important to choose parts that work well together to avoid bottlenecking issues.
What Is CPU Bottlenecking?

CPU bottlenecking happens when the CPU is the computer’s slowest part, slowing the overall performance.
Imagine a racing team where one runner is slower than the others; it holds back the whole team. Similarly, in a computer, if the CPU can’t keep up with other parts like the GPU or RAM, it slows down tasks.
This can occur due to an outdated CPU, heavy software, or demanding tasks exceeding the CPU’s capabilities. Identifying and addressing CPU bottlenecking is essential for maintaining smooth computer performance.
Components of a Computer System
A computer system consists of different parts that work together. These include the CPU, which processes information; the GPU, which is responsible for graphics; RAM, used for temporary storage; and storage devices like hard drives or SSDs, which are used for storage and storage. Each component plays a crucial role in the functioning of the computer.
What Are The Causes of CPU Bottlenecking?
- Outdated CPU: Using an old or low-performance CPU that needs help to keep up with modern software and tasks can lead to bottlenecking.
- Heavy Software Usage: Running resource-intensive programs or multitasking heavily can overwhelm the CPU’s processing capabilities, causing bottlenecking.
- Insufficient Cooling: Inadequate cooling solutions or improper ventilation can result in thermal throttling, where the CPU reduces its performance to prevent overheating, leading to bottlenecking.
- Incompatible Hardware: Pairing a powerful CPU with inconsistent or slow hardware components such as RAM or storage devices can create a bottleneck as the CPU waits for data from these components.
- Overclocking Issues: Overclocking the CPU beyond its stable limits without proper cooling or voltage adjustments can cause instability and performance degradation, resulting in bottlenecking during operation.
Types Of Motherboard Bottlenecks

1. Socket Compatibility
Socket compatibility refers to whether a CPU fits into a motherboard’s socket. They won’t work together if the CPU and motherboard have different sockets. It’s crucial to check compatibility before buying components.
2. VRM and Power Delivery
VRM, or voltage regulator module, manages power delivery to the CPU. A good VRM ensures a stable power supply, preventing CPU performance issues. Choosing a motherboard with a robust VRM is crucial for optimal CPU performance.
3. Memory Support
Memory support refers to the type and amount of RAM a motherboard can handle. Choosing a motherboard with sufficient memory support ensures smooth operation and prevents bottlenecking.
Matching the motherboard’s memory specifications with the RAM you intend to use for optimal performance is essential.
See Also: CPU Vdd Soc Current Optimization – Optimize CPU Power!
How Do You Choose A CPU to Avoid A Motherboard Bottleneck?
1. Research CPU and Motherboard Compatibility
Researching CPU and motherboard compatibility is crucial before building a computer. Ensure the CPU fits the motherboard’s socket and the motherboard supports the CPU’s features for optimal performance. Checking compatibility prevents bottlenecking issues and ensures smooth operation.
2. Consider CPU Power and Performance
When building a computer, consider the CPU’s power and performance. Choose a CPU that meets your needs and budget.
A powerful CPU ensures smooth multitasking and better performance in demanding tasks. Balancing power and cost is essential for an efficient system.
3. Assess Motherboard VRM Design
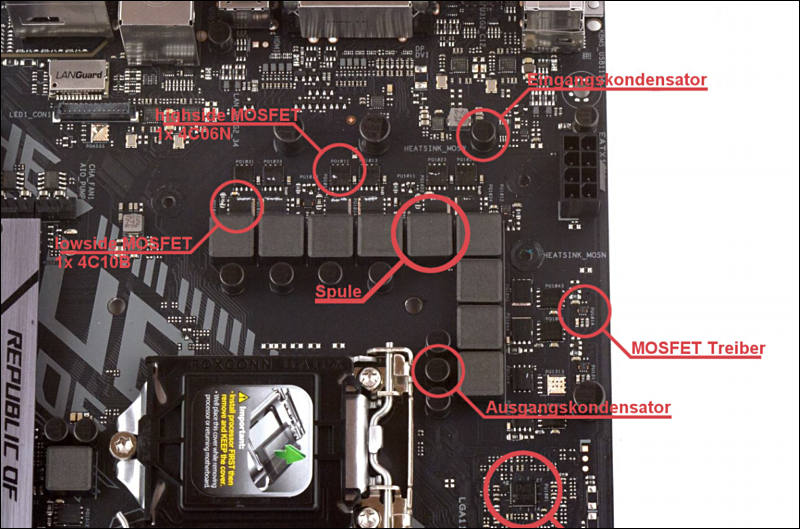
Evaluate the motherboard’s VRM design to ensure stable power delivery to the CPU. A robust VRM design prevents overheating and voltage fluctuations, optimizing CPU performance.
Choosing a motherboard with a reliable VRM design is crucial for a smooth computing experience.
4. Evaluate Memory Support
Check the motherboard’s memory support to ensure compatibility with your RAM. Verify the type, speed, and maximum capacity supported.
Choosing a motherboard with adequate memory support prevents compatibility issues and ensures optimal performance for your system.
5. Consider Expansion and Future Upgrades
When choosing a motherboard, consider its expansion slots and compatibility with future upgrades. Opt for a motherboard with ample expansion options like PCIe slots and sufficient RAM slots. Planning for future upgrades ensures the longevity and adaptability of your system.
6. Budget and Balance
When building a computer, consider your budget and balance it with performance needs. Choose components that offer the best value for your money.
Balancing cost and performance ensures a satisfactory computing experience without overspending.
Factors Contributing to CPU Bottleneck
- Outdated CPU: An older or slower CPU can limit overall system performance.
- Heavy Software Usage: Running resource-intensive programs can overwhelm the CPU.
- Insufficient RAM: Not having enough RAM can lead to bottlenecking as the CPU waits for data.
- Inadequate Cooling: Poor cooling solutions can cause the CPU to throttle, reducing performance.
- Incompatible Hardware: Pairing a powerful CPU with incompatible components can create bottlenecks.
- Overclocking Issues: Overclocking beyond stable limits can lead to instability and reduced performance.
- Software Optimization: Poorly optimized software can strain the CPU, causing bottlenecking.
- Background Processes: Running numerous background processes can consume CPU resources.
- Disk Fragmentation: Fragmented disks can slow down data access, affecting CPU performance.
- System Malware: Malware or viruses can consume CPU resources, causing bottlenecking.
See Also: Can I Use 70 Alcohol To Clean CPU: Optimal Cleaning Solution
Identifying Motherboard Bottleneck
Identifying a motherboard bottleneck involves checking its compatibility with other components like the CPU and RAM.
Look for outdated features like limited PCIe slots or slow RAM support. Poor VRM design or inadequate power delivery can also bottleneck performance.
Monitoring system performance for signs of underutilized CPU or RAM can help pinpoint motherboard bottlenecking issues.
Impact of Motherboard Bottleneck
A motherboard bottleneck can significantly affect overall system performance. It may lead to slower data transfer rates, limiting the speed of connected devices.
Incompatibility issues with CPU or RAM can cause system instability or crashes. Additionally, inadequate power delivery can result in CPU throttling, reducing processing power.
Addressing motherboard bottlenecking is crucial to ensure optimal performance and stability of the computer system.
Understanding Potential Bottlenecks
- Compatibility: Not all CPUs are compatible with all motherboards. The motherboard must support the CPU’s socket type and chipset. Installing a CPU on an incompatible motherboard can result in the system failing to boot or operating at reduced performance.
- VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) Quality: The VRM on the motherboard regulates the voltage supplied to the CPU. A poorly designed or inadequate VRM may need help providing sufficient CPU power, especially under heavy loads or overclocking scenarios. This can lead to instability and degraded CPU performance.
- PCIe Lane Configuration: The number and configuration of PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) lanes on the motherboard can impact the performance of components such as GPUs, storage devices, and expansion cards. Insufficient PCIe lanes or bottlenecked bandwidth can hinder the performance of devices connected to the motherboard, indirectly affecting CPU performance in tasks reliant on these devices.
- BIOS/UEFI Updates: The motherboard’s BIOS/UEFI firmware is crucial in optimizing system performance and compatibility. Outdated firmware may only partially support newer CPUs or incorporate performance-enhancing features and optimizations. Updating the BIOS/UEFI can improve CPU performance and stability.
- Thermal Management: Effective thermal management is essential for maintaining optimal CPU performance. The motherboard’s VRM and chipset cooling solutions and the layout of components on the motherboard can impact thermal dissipation. Inadequate cooling may result in thermal throttling, where the CPU reduces its clock speed to prevent overheating, thus limiting performance.
See Also: Is It Normal For CPU Clock Speed To Fluctuate – Guideline!
Conclusion
In The End,
A motherboard can bottleneck a CPU if compatibility or performance issues exist. However, carefully considering factors such as compatibility, VRM quality, PCIe lane configuration, BIOS/UEFI updates, and thermal management can mitigate these bottlenecks, ensuring optimal performance and stability of the computer system.
Related Questions
1. How Do I Know If My Motherboard Is Bottlenecking My CPU?
Look for signs like compatibility issues, slow performance despite a capable CPU, or limitations in features like PCIe lanes or RAM support.
2. What Can Bottleneck A CPU?
Factors like an outdated CPU, heavy software usage, insufficient RAM, inadequate cooling, incompatible hardware, or overclocking issues can all contribute to CPU bottlenecking.
3. Can Ram Bottleneck My CPU?
If the RAM is too slow or insufficient, it can bottleneck the CPU by not providing data quickly enough for processing.
4. Can A Motherboard Throttle A GPU?
Yes, if the motherboard doesn’t provide sufficient power or bandwidth to the GPU, it can throttle its performance, affecting overall graphics processing capabilities.
5. Can Any Motherboard Cause A CPU bottleneck?
No, not every motherboard will cause a CPU bottleneck. It depends on factors like compatibility, features, and quality of components.
6. Is It Possible To Upgrade Only The Motherboard To Overcome CPU bottlenecks?
No, upgrading only the motherboard may not necessarily overcome CPU bottlenecks. Other components like the CPU, RAM, and GPU significantly affect system performance.
7. What Causes A CPU Bottleneck?
Factors like an outdated CPU, heavy software usage, insufficient RAM, inadequate cooling, incompatible hardware, or overclocking issues can cause a CPU bottleneck.
8. Should I Always Buy The Most Expensive Motherboard To Avoid CPU bottlenecks?
Not necessarily. The most expensive motherboard may only sometimes be required to avoid CPU bottlenecks. Instead, prioritize compatibility, features, and quality within your budget.
Also Read
- Is 7 Days To Die CPU Or GPU Intensive – Check Gaming Issues!
- CPU Userbenchmark Bias – Investigate CPU Test Equality!
- Bad CPU Type In Executable Homebrew – Ultimate Guide In 2024

Hi everyone, Johns Jack here, your approachable tech aficionado! I’m passionate about CPUs and thrive on keeping up with the newest tech developments. Join me as we delve into the dynamic realm of technology! Visit: Techy Impacts